DATA LINEAGE. THE CRYSTAL BALL YOU ALWAYS HAVE BEEN LOOKING FOR?
Data is king. Businesses rely on data to make decisions, understand their customers, and improve their operations. However, in complex organizations, it can be difficult to get insight into relevant data flows.
There are a number of reasons why this is the case. First, complex organizations often have a large number of data sources. This can make it difficult to track the movement of data between different systems and applications. Second, data flows in complex organizations can be complex and dynamic. This means that the path that data takes can change over time, making it difficult to keep track of. Third, data in complex organizations is often siloed. This means that data is stored in different systems and applications, making it difficult to get a holistic view of the data.
As a result of these challenges, it can be difficult to get insight into data flows in complex organizations. This can make it difficult to ensure the quality of data, comply with regulations, and make informed decisions. Despite these challenges, there are a number of things that organizations can do to get insight into data flows. Data lineage is typically a fundamental capability.
What is Data Lineage?
Data lineage is the tracking of data as it flows through an organization’s systems and processes. It provides a detailed record of the data’s origin, transformation, and destination. Data lineage is important for a number of reasons, including:
- Data quality: Data lineage can help to ensure the quality of data by providing a way to track its history and identify any potential problems. For example, if a data point changes unexpectedly, data lineage can be used to trace back the change and identify the source of the problem.
- Compliance: Data lineage can help organizations to comply with regulations that require them to track the movement of data. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires organizations to track the personal data of their customers. Data lineage can help organizations to meet this requirement by providing a record of how personal data is collected, used, and stored.
- Auditing: Data lineage can be used to audit data flows and identify potential security risks. For example, if an organization is concerned about the possibility of a data breach, data lineage can be used to track the movement of sensitive data and identify any potential vulnerabilities.
- Business intelligence: Data lineage can help organizations to gain insights into their data by providing a way to track the relationships between different data sets. For example, data lineage can be used to identify which data sets are used to calculate a particular metric. This information can then be used to improve the accuracy of the metric and make better business decisions.
Benefits
- Improved data governance: Data lineage can help organizations to improve their data governance practices by providing a way to track the ownership, access, and usage of data. This information can then be used to develop and enforce data policies and procedures.
- Reduced risk of data loss: Data lineage can help to reduce the risk of data loss by providing a way to track the location of data. This information can then be used to recover data in the event of a loss or corruption.
- Increased data agility: Data lineage can help organizations to become more data agile by providing a way to track the changes to data. This information can then be used to update data models and applications as needed.
How to Implement Data Lineage
There are a number of ways to implement data lineage. One way is to use a data lineage tool. These tools can help to automate the tracking of data flows and provide a visual representation of data lineage. Another way to implement data lineage is to manually track data flows. This can be done by creating spreadsheets or diagrams that track the movement of data.
The best way to implement data lineage will depend on the specific needs of the organization. However, all organizations should consider implementing data lineage to improve the quality and usability of their data.
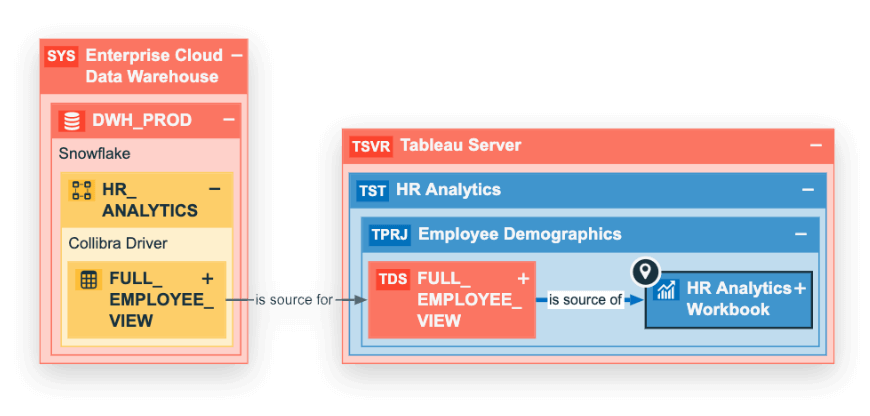
A sample data lineage diagram illustrating the high-level data flow between a Tableau Workbook and a Snowflake datawarehouse.
Conclusion
In summary, data lineage is an important tool for organizations that want to ensure the quality, compliance, security, and usability of their data. By tracking the movement of data, data lineage can help organizations to identify and address problems, comply with regulations, and gain insights into their data.